Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
柴田 薫
波紋, 28(1), p.26 - 28, 2018/02
背面散乱中性子分光器の系譜とダイナミクス解析装置DNAの仕様を簡単に紹介する。DNA分光器は大強度陽子加速器施設(J-PARC)物質・生命科学実験施設(MLF)のパルス中性子源に設置されたSi結晶アナライザーを用いた飛行時間型(TOF)背面散乱分光器(n-BSS)である。DNA分光器と同系の、世界中で稼働中もしくは稼働していた主な研究用原子炉線源設置型およびパルス線源設置型の背面反射結晶アナライザー型高エネルギー分解能中性子分光器の概要を説明し、その中でのDNA分光器の特徴について解説した。
柴田 薫; 高橋 伸明*; 川北 至信; 松浦 直人*; 富永 大輝*; 山田 武*; 中島 健次; 小林 誠*; 稲村 泰弘
no journal, ,
J-PARCセンター、物質・生命科学実験施設に設置され eVの高エネルギー分解能を実現したSi結晶アナライザー背面反射TOF型分光器DNAにおける広帯域エネルギースペクトル測定のための、パルス整形チョッパーの複数スリットを利用した同時多重入射バンドを用いる測定方法の開発を行った。コミッショニング測定および共用実験での適用例を交えて報告予定である。
eVの高エネルギー分解能を実現したSi結晶アナライザー背面反射TOF型分光器DNAにおける広帯域エネルギースペクトル測定のための、パルス整形チョッパーの複数スリットを利用した同時多重入射バンドを用いる測定方法の開発を行った。コミッショニング測定および共用実験での適用例を交えて報告予定である。
柴田 薫
no journal, ,
飛行時間型背面反射分光器DNAはJ-PARCセンター物質生命科学実験施設MLF中性子源に建設され2012年から測定を開始した。DNA分光器はパルス整形のため高速回転ダブルディスクチョッパーを備えた入射パルス幅を調整可能な背面反射分光器として、世界中のスポレーションパルス中性子源に設置されている装置の中でユニークな装置となっている。一方中性子吸収剤を背面に不塗布したSi結晶アナライザーはバックグランド散乱を低減させS/N比は~100,000.を達成している。これらの性能向上により、ナノ秒時間スケールまたは eVエネルギー範囲の生体高分子、機能性物質、強相関電子系の原子、スピン運動まで研究分野を広げている。これらのDNA分光器の特質すべき性能とその研究応用成果について発表予定である。
eVエネルギー範囲の生体高分子、機能性物質、強相関電子系の原子、スピン運動まで研究分野を広げている。これらのDNA分光器の特質すべき性能とその研究応用成果について発表予定である。
 eV高エネルギー分解能TOF型Si結晶アナライザーBackscattering分光器DNA(J-PARC)における非弾性・準弾性散乱研究の現状
eV高エネルギー分解能TOF型Si結晶アナライザーBackscattering分光器DNA(J-PARC)における非弾性・準弾性散乱研究の現状柴田 薫; 川北 至信; 中川 洋; 山田 武*; 富永 大輝*; 松浦 直人*
no journal, ,
J-PARCセンター物質・生命科学実験施設MLFに設置されているSi結晶アナライザー背面反射TOF型高エネルギー分解能分光器DNAは、1.6micro eV以下の高エネルギー分解能を実現し高S/N比で広帯域に亘るmicro eV分解の非弾性散乱・準弾性散乱測定を世界に先駆けて実現した。本発表では、DNA分光器の平成29年度の現状と新たな研究成果を報告書する。
柴田 薫
no journal, ,
シリコン結晶アナライザーは、高エネルギー分解能の中性子非弾性後方散乱分光器の重要な分光デバイスで、その仕様は、分光器のエネルギー分解能とバックグラウンドを決定すると考えられている。エネルギー分解能を低下させることなく高S/N比のスペクトル測定を達成するために、構成するシリコンウエハの裏面に中性子吸収材料をコーティングした新しいシリコン結晶アナライザーを独自に新規開発・製作した。これを、J-PARCセンター物質生命科学実験施設のパルス中性子源に設置したダイナミクス解析装置DNA分光器の結晶アナライザーに使用して目的の性能を達成することが確認できた。
川北 至信; 松浦 直人*; 富永 大輝*; 山田 武*; 玉造 博夢; 中川 洋; 大内 啓一*
no journal, ,
DNA is a time-of-flight backscattering spectrometer installed at BL02 neutron port seeing a coupled moderator of Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) aiming at revealing pico to nano second dynamics in a wide field of basic sciences and industrial applications including soft matter, bio-molecules, chemical molecules, battery, catalyst, and magnetism. Recent scientific outcomes exhibit a wide variety of research fields and methods of experiments and data analyses. In my presentation, current status and upgrade plan in near future of the DNA spectrometer and typical experiments demonstrating its performance will be presented.
川北 至信; 松浦 直人*; 富永 大輝*; 山田 武*; 玉造 博夢; 中川 洋; 大内 啓一*
no journal, ,
DNA is a TOF type Si crystal analyzer backscattering spectrometer installed at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) spallation source. DNA uses a pulse-shaping chopper to extract sharp pulsed neutron from strong but broad spectrum of coupled moderator, which achieves good energy resolution (~2.4 micro-eV) and large neutron flux simultaneously. In addition, time-of-flight technique allows us to go high energy transfers of about 1500 micro-eV. Furthermore, the signal-to-noise ratio at DNA achieves 10 , which enables to covers a variety of research fields from biomaterials with small scattering amplitudes or with small quantities of samples (of the order of milligrams). DNA has Si111 analyzers, which allows to access momentum transfer range from 0.08 to 1.86
, which enables to covers a variety of research fields from biomaterials with small scattering amplitudes or with small quantities of samples (of the order of milligrams). DNA has Si111 analyzers, which allows to access momentum transfer range from 0.08 to 1.86 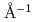 . Currently, we are installing Si311 analyzers covering momentum transfer from 1.79 to 3.39
. Currently, we are installing Si311 analyzers covering momentum transfer from 1.79 to 3.39 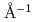 , which overlaps Q-region of Si111. We are developing various sample environments, such as magnet, automatic sample changers, furnace, humidity controller, and radial collimators. We are also promoting the Internet of Things (IoT) of the equipment due to strong demands of remote experiments from COVID-19. We will show the current status and upgrade plan of DNA.
, which overlaps Q-region of Si111. We are developing various sample environments, such as magnet, automatic sample changers, furnace, humidity controller, and radial collimators. We are also promoting the Internet of Things (IoT) of the equipment due to strong demands of remote experiments from COVID-19. We will show the current status and upgrade plan of DNA.